Utilizing Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Constructing Intelligent Software Robots
In this article, we’ll explore the history of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in banking, tracking its evolution from initial robot deployment to a crucial in enhancing business process efficiency. We will look at how RPA has shaped routine and intelligent decision-making processes, leading to increased productivity and cost savings in banking operations.
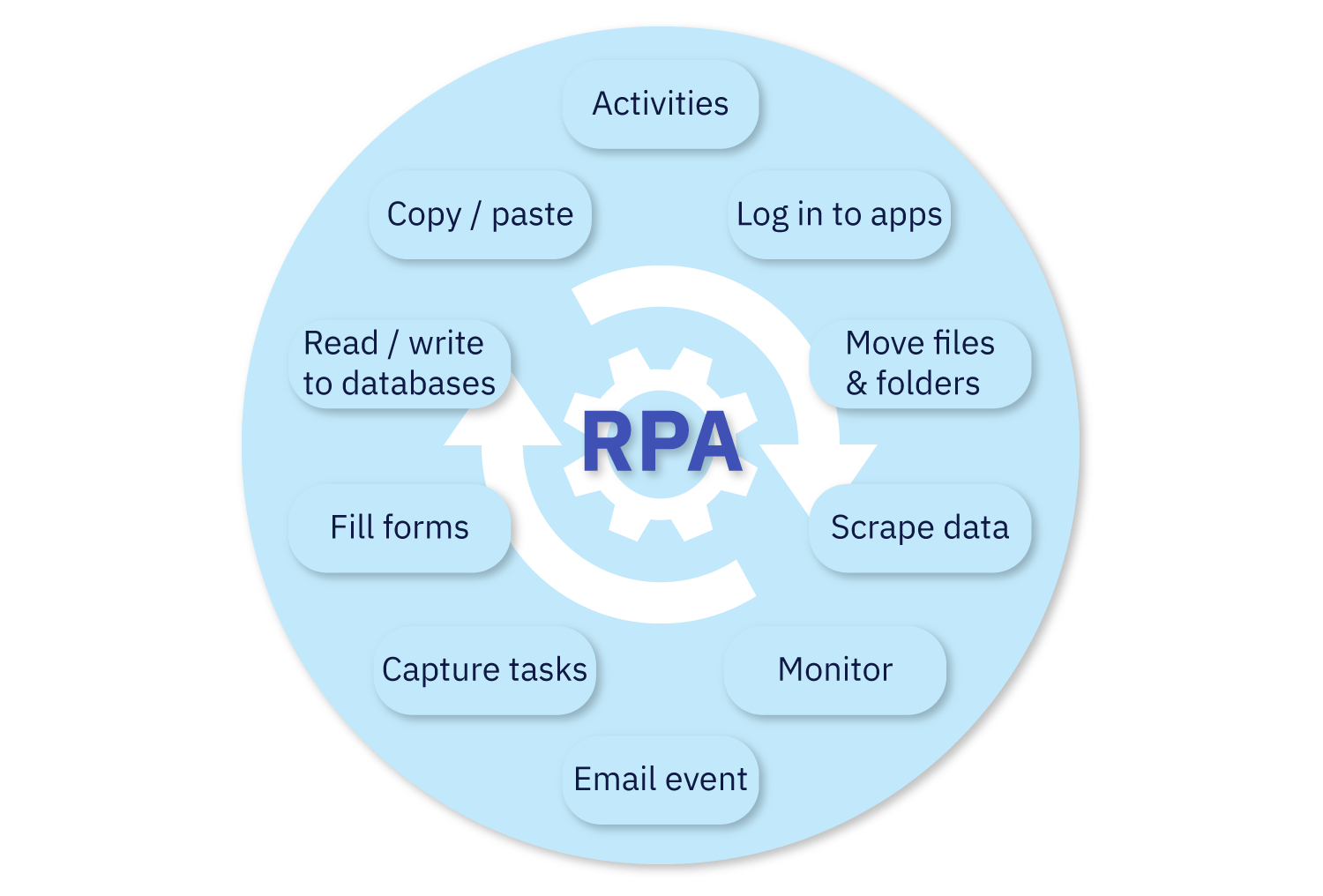
Let’s travel back in time and revisit the origins of business process automation in the banking sector. From the initial days of deploying robots in banks, the primary focus was on enhancing efficiency and optimizing specific tasks. At that time, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, enabling companies to boost productivity, improve efficiency, and achieve cost savings.
Robots were responsible for automating processes such as gathering information from sources, moving files and folders, reading from and writing to databases, filling out forms in various applications, and more.
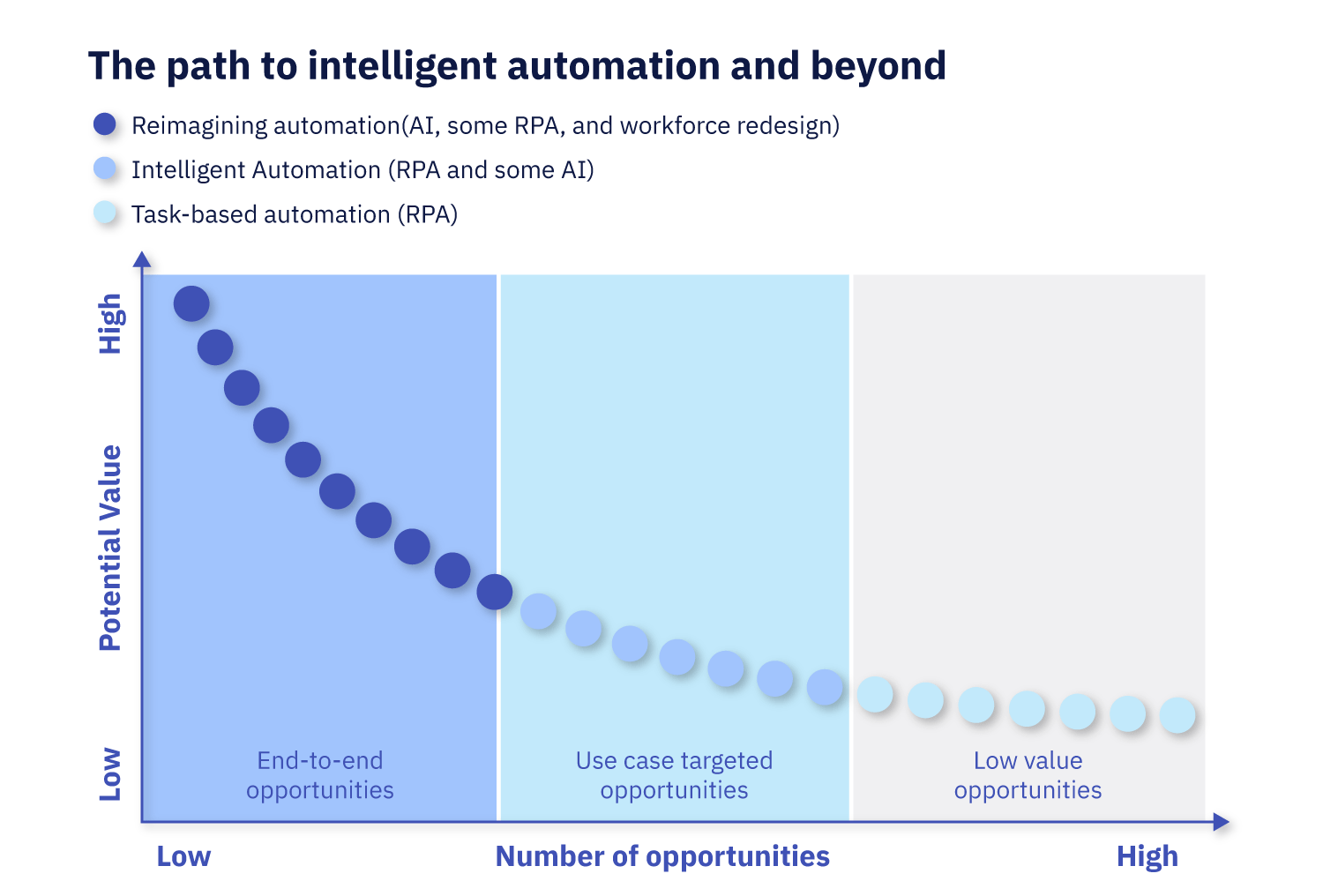
RPA has delivered increased productivity, efficiency, and cost savings for easily automatable processes. However, RPA does not address all your automation needs. A significant number of processes still require more intelligent decision-making. The next stage in this evolution is the concept of Intelligent Process Automation (IPA). In case of RPA, the number of processes suitable for automation is higher, but the returns are lower than from IPA where the number of processes is lower, but the returns are higher.
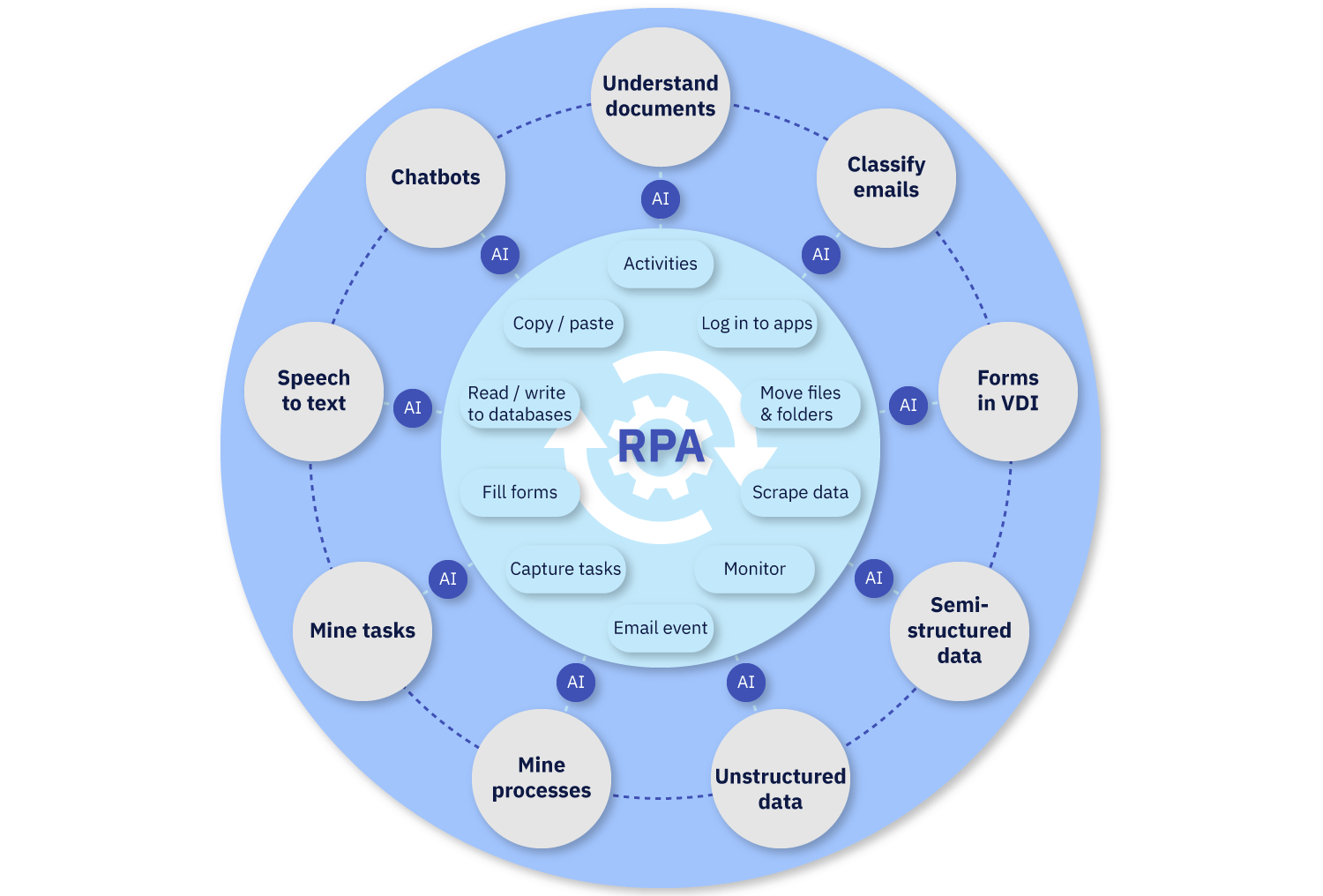
IPA broadens the spectrum of tasks to be assigned to a robot
IPA integrates technologies such as RPA, machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and in certain cases, computer vision. The advancement of artificial intelligence technologies has empowered robots to process unstructured documents, classify messages, recognize signatures, integrate with chatbots, and more.
Exploring the evolution embodied in IPA, we’ll examine how it transforms and optimizes business processes at banks, ensuring not only increased productivity but also the creation of richer and higher-quality interactions.
Let’s delve into specific artificial intelligence algorithms and examples of their use for process automation at a bank.
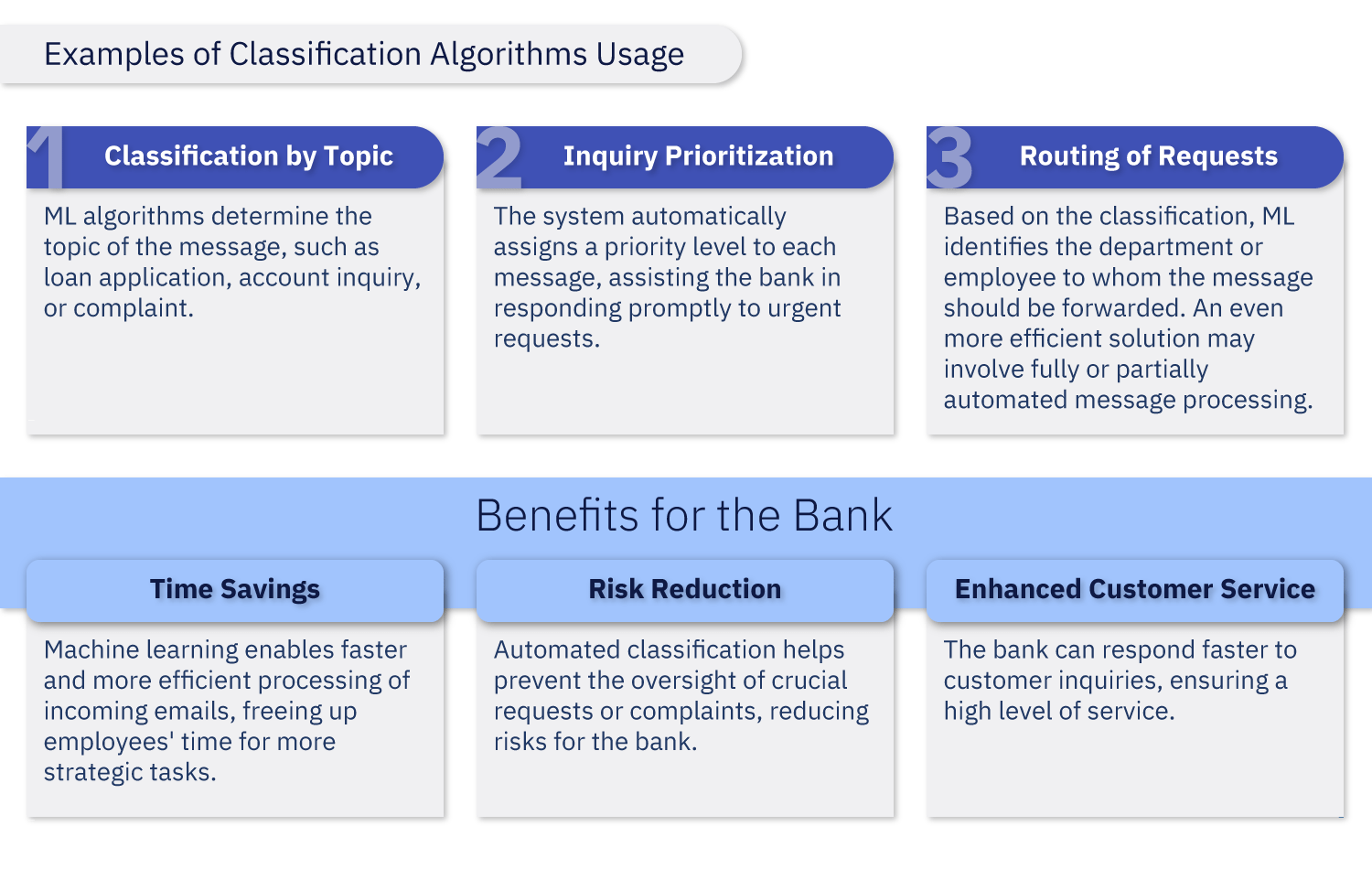
Classification Algorithms
In the banking sector, a large volume of electronic messages from clients, partners, and other stakeholders comes daily. Instead of manual processing of each message, the bank implements a machine learning system for their automatic classification, followed by routing either to the appropriate handler or to a corresponding automated tool.
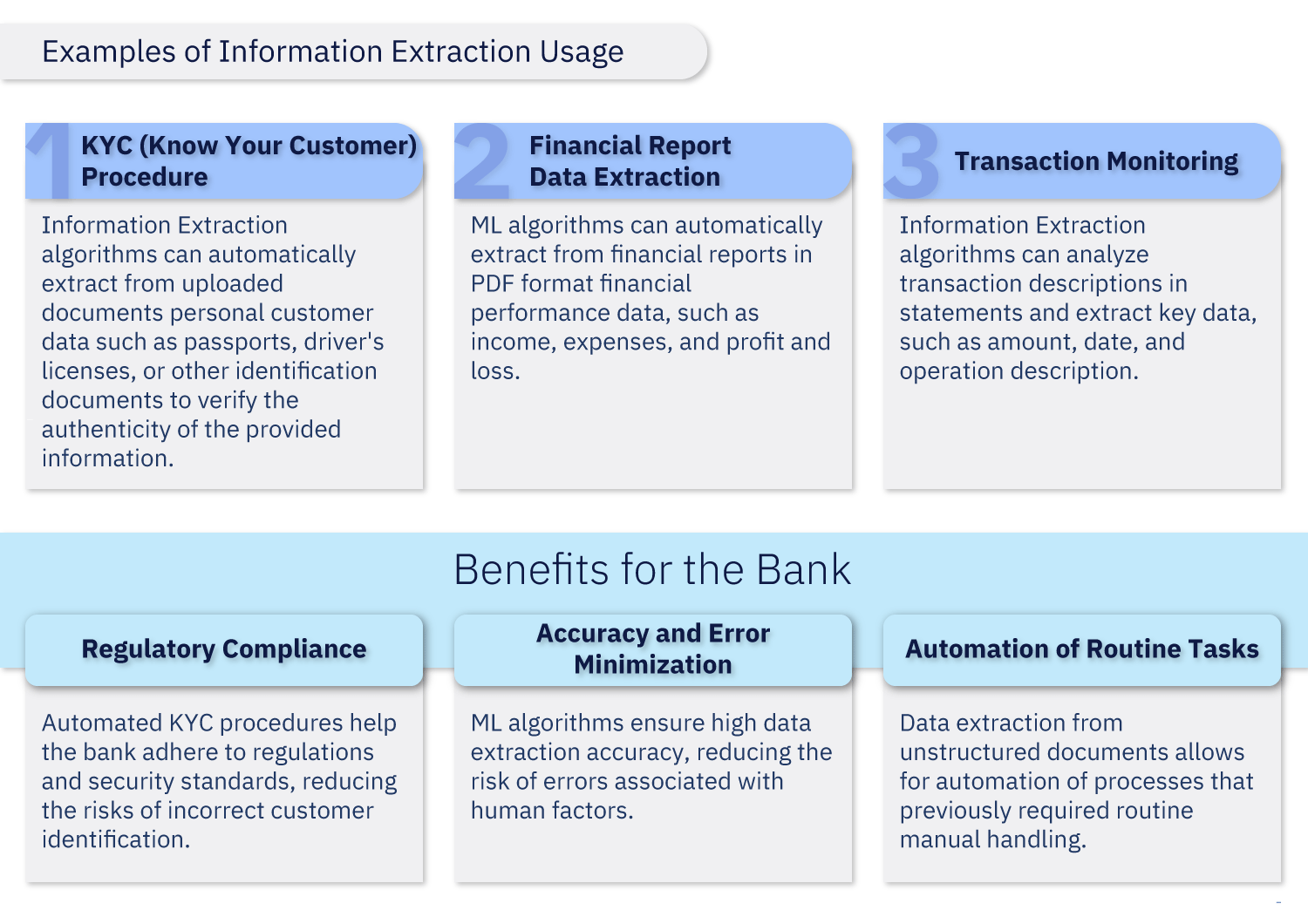
Information Extraction
Let’s explore another practical example of applying machine learning in banking operations.
Example: Data Extraction from Unstructured Documents
In the banking sector, a vast amount of data is stored in unstructured or semi-structured documents, such as PDF files, text documents within email bodies, and other formats. The information contained in these documents is often crucial for various business processes.
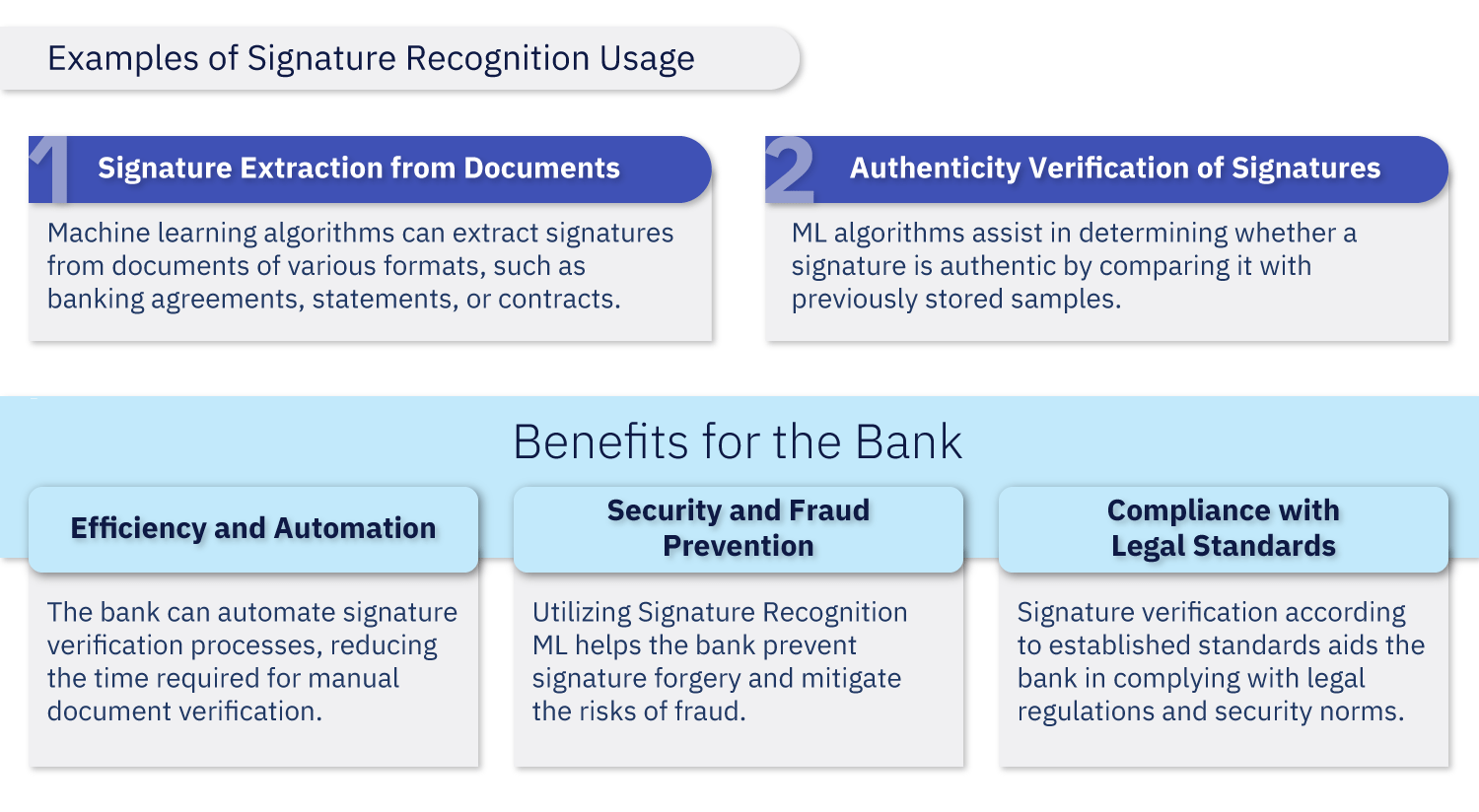
Identification and Signature Recognition
Let’s continue examining specific examples of applying machine learning in the banking sector.
In banking operations, documents signed by clients, employees, or partners are commonplace. The process of signature recognition becomes crucial in business processes where the authenticity and genuineness of the signature are essential.
Click to read the second part, GPT Models in the Banking Sector: Revolution in Artificial Intelligence